This tutorial is for beginners who want to learn steps to create EJB persistence application with Eclipse and Jboss.
Tools used
Eclipse (Galileo)
Jboss-5.1.0.GA
MySQL database
First of all I'll create a database called studentmgt_db. You can use MySQL GUI tool like MySQL Query Browser or MySQL Work Bench to create a database.
Then I'm going to create a datasource. Go to your jboss directory ..jboss-5.1.0.GA\docs\examples\jca inside that folder there is file called mysql-ds.xml. I copied that file to ...jboss-5.1.0.GA\server\default\deploy. Then you can add your database details to that file.
mysql-ds.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- $Id: mysql-ds.xml 41017 2006-02-07 14:26:14Z acoliver $ -->
<!-- Datasource config for MySQL using 3.0.9 available from:
http://www.mysql.com/downloads/api-jdbc-stable.html
-->
<datasources>
<local-tx-datasource>
<jndi-name>StudentMgtDS</jndi-name>
<connection-url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/studentmgt_db</connection-url>
<driver-class>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver-class>
<user-name>root</user-name>
<password>123</password>
<exception-sorter-class-name>org.jboss.resource.adapter.jdbc.vendor.MySQLExceptionSorter</exception-sorter-class-name>
<!-- should only be used on drivers after 3.22.1 with "ping" support
<valid-connection-checker-class-name>org.jboss.resource.adapter.jdbc.vendor.MySQLValidConnectionChecker</valid-connection-checker-class-name>
-->
<!-- sql to call when connection is created
<new-connection-sql>some arbitrary sql</new-connection-sql>
-->
<!-- sql to call on an existing pooled connection when it is obtained from pool - MySQLValidConnectionChecker is preferred for newer drivers
<check-valid-connection-sql>some arbitrary sql</check-valid-connection-sql>
-->
<!-- corresponding type-mapping in the standardjbosscmp-jdbc.xml (optional) -->
<metadata>
<type-mapping>mySQL</type-mapping>
</metadata>
</local-tx-datasource>
</datasources>
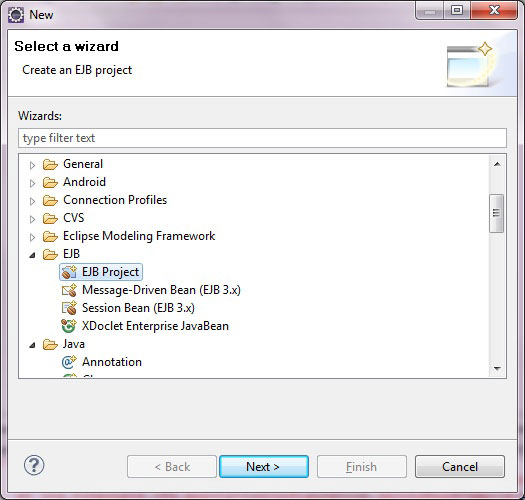
Now create EJB project.Create a new EJB project called StudentManagementEJB. I use JBoss server as application server.
Create a xml file called persistence.xml in META-INF directory.
persistence.xml
Then we have to create an Entity class. Right click on the project -> New -> Class<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"> <persistence-unit name="StudentMgtPU" transaction-type="JTA"> <jta-data-source>java:/StudentMgtDS</jta-data-source> <properties> <property name="hibernate.dialect" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect" /> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create" /> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
- Entity Class must have @Entity annotaion
- Must have a public or protected no-arg constructor
- If it passed as a detached object through a remote interface, Must implement Serializable
- Must have an id annotated with @Id
Student.java
package com.sameera.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name = "id")
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "first_name", length = 100)
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name", length = 100)
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email", length = 100)
private String email;
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
Create session beans.I create a Stateless session bean with Local interface.
I added business methods and added add student code.
ManageStudentSessionBeanLocal.java
package com.sameera.session;
import javax.ejb.Local;
import com.sameera.domain.Student;
/**
*
* @author Sameera Jayasekara
*
*/
@Local
public interface ManageStudentSessionBeanLocal {
public boolean addStudent(Student Student);
}
ManageStudentSessionBean.java
package com.sameera.session;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import com.sameera.domain.Student;
/**
* Session Bean implementation class ManageStudentSessionBean
*
* @author Sameera Jayasekara
*/
@Stateless
public class ManageStudentSessionBean implements ManageStudentSessionBeanLocal {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public boolean addStudent(Student student) {
entityManager.persist(student);
return true;
}
}
Run EJB application on Jboss server.See the server console JNDI bindings.
Now see the database. Student table is created.
Now start working on web application.
File -> New -> Dynamic Web Project
Go next Select 'Generate web.xml deployment descriptor' and finish.
Right click on web content and create a new jsp called index.jsp.
index.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>EJB3 JPA Jboss - codesstore.blogspot.com</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="ManageStudentServlet" method="POST">
<table border="0" width="100%">
<tr>
<td colspan="3"> ${message}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>First Name</td>
<td>:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="fname" value="" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Last Name</td>
<td>:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="lname" value="" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Email</td>
<td>:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="email" value="" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Add" name="Add" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Create a servlet to handle the request.
File -> New -> Servlet
Before calling Enterprise beans we have to add the ejb project to build path.
Go to projects tab and add StudentManagementEJB project.
ManageStudentServlet.java
package com.sameera.controller;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.sameera.domain.Student;
import com.sameera.session.ManageStudentSessionBeanLocal;
/**
*
* @author Sameera Jayasekara
*
*/
public class ManageStudentServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private ManageStudentSessionBeanLocal manageStudentSessionBeanLocal;
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
try {
Context context = new InitialContext();
manageStudentSessionBeanLocal = (ManageStudentSessionBeanLocal) context
.lookup("ManageStudentSessionBean/local");
} catch (NamingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String message = "";
String firstName = request.getParameter("fname");
String lastName = request.getParameter("lname");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
Student student = new Student();
student.setFirstName(firstName);
student.setLastName(lastName);
student.setEmail(email);
if (manageStudentSessionBeanLocal.addStudent(student)) {
message = "Student Successfuly Added";
} else {
message = "Student Adding Failed";
}
request.setAttribute("message", message);
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("index.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
I looked up ManageStudentSessionBean/local. You can see server console to find JNDI bindings(see image given above)You can use @EJB annotaions to dependancy injection in a servlet but I tried it with JBoss that didn't work.Then I used @EJB(mappedName="Test"), @EJB with mappedName attribute( @Stateless(mappedName="Test") also used).Then it worked with remote interface. But I prefer JNDI lookup.
web.xml configuration file looks like this.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>StudentManagementWeb</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<description></description>
<display-name>ManageStudentServlet</display-name>
<servlet-name>ManageStudentServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.sameera.controller.ManageStudentServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ManageStudentServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ManageStudentServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Now You can run the web application.Check the database data will be added.
Project structure in Eclipse
Note : I put mysql-connector-java-5.1.5-bin.jar to ...jboss-5.1.0.GA\server\default\lib














Hi Sameera,
ReplyDeleteThanks for the post . I am using GlassFish with JPA + Eclipse. Would you please make a tutorial on this.
Thanks
David
PS: are you available on Skype?
Simple CRUD with JSF and Hibernate - GeekOnJava:
DeleteHibernate CRUD example using HQL query language:
Solve QuerySyntaxException in Hibetnate:
All are superb articles... Thanks a lot
ReplyDeleteHi Sameera, good example, now we can use netbeans and generate all these codings.....
ReplyDeleteYea. See My EJB JPA Netbeans tutorial http://codesstore.blogspot.com/2012/07/ejb3-and-jpa-step-by-step-tutorial_05.html
DeleteHi Sameera,
ReplyDeleteIm a new comer to the JavaBeans.
I got the following error when starting the JBoss server. What should I do?
12:12:13,843 ERROR [SchemaExport] schema export unsuccessful
Hi Sapumal. U got the answer? :D
Deletegreat work
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThanks Sameera...it helped me alot...while learning JPA...
ReplyDeletemachan sammeera i tried it form Postgres Sql , but not creating tables ,what is the jdbc connector for Postgres
ReplyDeletethanks ,im also from UCSC. Good luck
I haven't tried with Postgres,
DeleteCheck this value is 'create'
property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create"
Driver may be
postgresql-.....jdbc4.jar
Driver class: org.postgresql.Driver
Connection URL:
jdbc:postgresql://[servername]:[port]/[database name]
thanks it is working...
DeleteGreat work, I have a problem with the steps, I'm using Jboss as 7.1, and the directorys jboss-as-7.1/docs/examples/jca and jboss-7.1server/default/deploy don't exist in this version, the file mysql-ds.xml is standalone.xml in this version; how can I do the step of the jboss when you copy the file, where should I copy it?
ReplyDeleteThanks for the tutorial, it's excellent
Great work! Simple and Nice Article.
ReplyDeleteThis is good stuff Sameera. well presented and easy to understand !
ReplyDeleteHTTP method POST is not supported by this URL
ReplyDeleteplease help me
Delete